- Published on
What Materials Can Be Cut Using A Laser Cutting Machine
- Authors

- Name
- Ryan Carter
Laser cutting technology is an efficient, precise, and widely used cutting method in various industries. Laser cutting machines can be used to cut many different types of materials, from metals to non-metals, and from thin sheets to thick blocks. However, there are also some materials that are not suitable for laser cutting due to their characteristics. This article will introduce the types of materials that laser cutting machines can cut and discuss the materials that are not suitable for cutting.
What Materials Can Be Laser Cut
Laser cutting is a highly versatile process that can be applied to a variety of materials. Here are some common materials that can be effectively laser cut.
Metallic Material
Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is one of the common laser cutting materials. Its advantages include high strength, corrosion resistance, and high-temperature resistance. Laser cutting allows for precise cuts, suitable for areas such as manufacturing, construction, and automotive engineering.
Aluminum
Aluminum is another commonly used metal material that is also suitable for laser cutting. Laser-cut aluminum enables high-quality cut edges and is suitable for manufacturing aerospace, transportation electronic equipment, and other fields.
Carbon Steel
Carbon steel is one of the ideal materials for laser cutting and is widely used in manufacturing. Laser cutting enables high-speed, high-quality cutting, suitable for automobile manufacturing, shipbuilding and machining, and other fields.
Non-metallic Materials
Wood
Laser cutting is suitable for cutting all types of wood, including plywood, density board, and solid wood. Laser cutting wood allows for precise cuts and is widely used in furniture manufacturing, handicraft production, architectural decoration, and other fields.
Acrylic
Acrylic is a clear and durable plastic material suitable for laser cutting. Laser cutting allows for smooth, crisp cut edges, suitable for areas such as advertising signs, exhibits, and artwork production.
Rubber
Rubber can also be processed by laser cutting and used to make seals, gaskets, rubber products, etc. Laser cutting can achieve a high-precision, high-efficiency cutting process.
Other Materials
Plastic
Many plastic materials can be processed by laser cutting, such as polyethylene, polypropylene, and polycarbonate. Laser cutting can achieve precise cuts and is suitable for areas such as plastic product manufacturing, the packaging industry, and the electronics industry.
Glass
Laser cutting can be used to cut thin glass, but may not be suitable for thick glass. Glass cutting usually uses other processing methods, such as grinding or cutting.
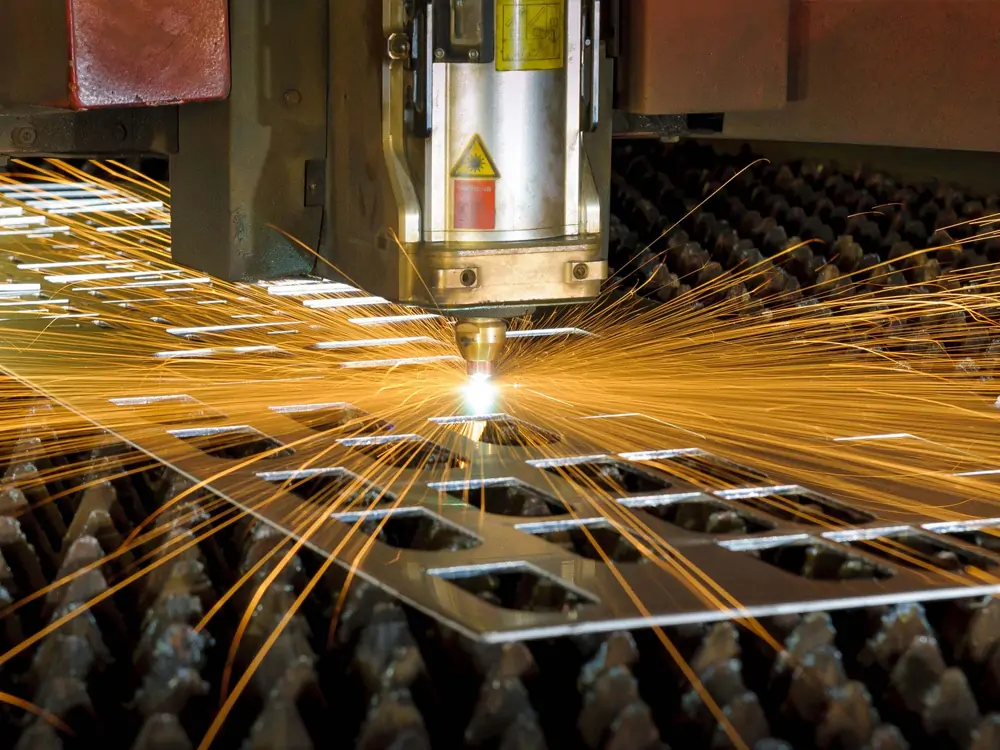

Materials That Cannot Be Laser Cut
Laser cutting technology can be used to cut many different types of materials. However, not all materials can be laser cut. Some materials may present difficulties or limitations for laser cutting due to their particular properties, structure, or composition. Next, we'll look at some materials that cannot be laser cut.
Transparent Material
Lasers are generally not effective at cutting transparent materials. Transparent materials such as crystal and glass are highly penetrable to laser light. Laser beams cannot be absorbed and reflected by transparent materials. Therefore, transparent materials are not suitable for laser cutting.
Diamonds And Gemstones
Diamond is one of the hardest natural materials on earth. Their hardness and stability make it difficult for a laser to apply enough force to cut. Laser cutting often relies on the process of melting, evaporating, or oxidizing the material, which is difficult with extremely hard diamonds.
Multilayer Composite Materials
Composite materials may be composed of layers of many different materials, some of which may not be suitable for laser cutting or may require specific laser parameters.
Reflective Metal
The main reason reflective metals are not suitable for direct use with conventional laser cutting techniques is their high reflectivity. This means that the laser beam will be mostly reflected when it hits the metal surface, rather than being effectively absorbed and converted into heat. Reflective metals, therefore, cannot generate enough heat energy to cut.
Heat-Sensitive Materials
Heat-sensitive materials are sensitive to high temperatures. Laser cutting produces high temperatures. Therefore, laser cutting can easily cause heat-sensitive materials to be heated, deformed, carbonized, or burned, thereby damaging the cutting edges and the structure of the material.
Application Industries of Laser Cutting
Laser cutting has the advantages of high precision, high efficiency, low deformation, and strong flexibility. Therefore, laser cutting technology has been widely used in many fields. It utilizes high-energy density laser beams to cut, cut, and engrave different types of materials. Here are some of the main application areas for laser cutting.
Metal Processing:
- Laser cutting is widely used for cutting metal sheets, such as steel, aluminum, stainless steel copper, etc. It can achieve high precision, high speed, and complex geometric shape cutting.
- Laser cutting can also be used to cut metal pipes, suitable for manufacturing pipes, car exhaust systems, etc.
Wood And Plastic Processing:
- Laser cutting can be used to cut and engrave wood for furniture manufacturing, art production, etc.
- Laser cutting can cut various types of plastics with high precision and is widely used in plastic product processing.
Electronic Device Manufacturing:
- Circuit board cutting: Laser cutting is used to cut and process circuit boards, which can achieve micro-size and high-density cutting.
- Semiconductor processing: Laser cutting can be used to cut and process semiconductor materials for manufacturing electronic devices.
Textile Processing:
- Laser cutting can be used to cut cloth, leather, and textiles. It can improve cutting efficiency and accuracy and is suitable for clothing manufacturing, etc.
Medical Device Manufacturing:
- Laser cutting can be used to manufacture parts for medical devices, such as precision surgical tools, implants, etc.
Automobile Manufacturing:
- Laser cutting is widely used in automobile manufacturing, such as cutting body parts, brake discs, etc.
Aerospace Industry:
- Laser cutting is used in the aerospace field to cut various aviation parts, such as wings, engine parts, etc.
Construction And Building Materials Manufacturing:
- Laser cutting is used to cut construction materials, such as steel structures, aluminum, glass, etc.

Conclusion
The emergence and development of laser cutting technology have brought about earth-shaking changes to many industries. Laser cutting is not only efficient, precise, and controllable but also can be applied to the processing of a variety of materials. Metal materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, carbon steel, etc., are often widely used in laser cutting technology, significantly improving their processing accuracy and quality. Additionally, non-metallic materials such as wood, acrylic, etc., also benefit from laser cutting technology, providing more innovation possibilities in various fields.
However, we also recognize that not all materials are suitable for laser cutting. Some highly reflective metals and heat-sensitive materials are not suitable for direct laser cutting technology due to their special physical properties. This prompts us to continuously explore and develop new processing technologies to